Struggling with insomnia while on antidepressants? You’re not alone. Many SSRI and SNRI users turn to melatonin as a sleep aid, hoping for natural relief. But how safe is it? This guide examines the melatonin antidepressant interaction in depth—uncovering potential benefits, side effects, and risks like serotonin syndrome. We’ll break down what the science says and how to approach melatonin use if you’re taking common SSRIs like fluoxetine or SNRIs such as duloxetine.
Quick Summary: Melatonin + Antidepressants Interaction
| Aspect | Key Insight |
|---|---|
| Primary Concern | Potential for reduced antidepressant efficacy and serotonin syndrome risk |
| Potential Benefits | May enhance antidepressant effects and improve sleep |
| Main Risks | Excessive sedation, serotonin syndrome, blood pressure spikes |
| Recommended Dose | ≤5 mg/day for adults (unless directed otherwise) |
| Usage Advice | Always consult a healthcare provider first |
| Interaction Level | Moderate (per Drugs.com and NHS guidelines) |
How Melatonin Affects Sleep and Mood Regulation

Melatonin is a hormone secreted by the pineal gland that helps regulate circadian rhythm and sleep-wake cycles. Its role as a natural sleep aid has made it a popular supplement—especially among those dealing with antidepressant-induced insomnia. Research also hints at melatonin’s ability to influence mood and emotional regulation, raising questions about how it interacts with psychotropic medications.
Some SSRI users report disrupted sleep, a side effect supported by data from sertraline (Zoloft) users, where up to 20% experience insomnia. This overlap in purpose—regulating mood and sleep—makes the interaction between melatonin and antidepressants particularly complex.
Synergistic Effects: Can Melatonin Enhance Antidepressants?
Potential Mood Benefits
Animal studies suggest that combining melatonin with SSRIs like fluoxetine could boost antidepressant outcomes. One Frontiers in Neuroscience study found enhanced BDNF levels and TrkB signaling when melatonin was combined with fluoxetine, pointing to potential synergistic mood improvements.
Another study published in PubMed observed improved depression markers in zebrafish when venlafaxine (an SNRI) was used with melatonin, indicating promising additive effects.
Sleep Improvement in Antidepressant Users
Given melatonin’s core role in circadian regulation, it’s no surprise that it may help offset sleep disturbances from antidepressants. Clinical resources like MedicineNet note that combining melatonin with SSRIs could improve overall sleep quality—but always with caution.
Key Risks of Combining Melatonin with SSRIs or SNRIs
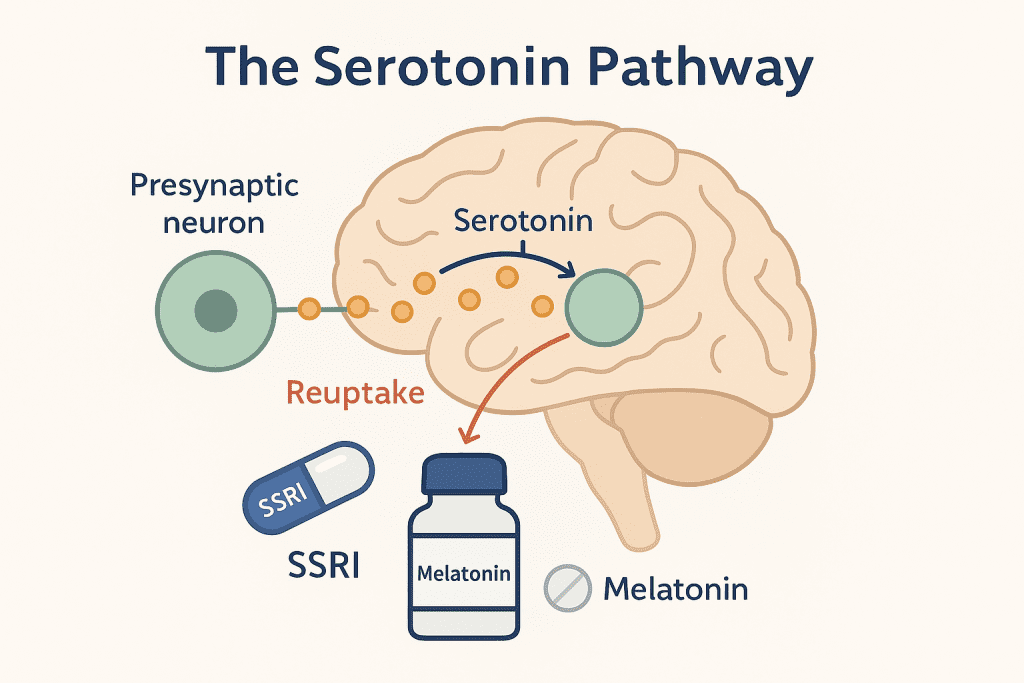
Serotonin Syndrome: A Rare but Serious Risk
Melatonin may influence serotonin indirectly. When combined with SSRIs or SNRIs, this can—in rare cases—lead to serotonin syndrome. According to Mayo Clinic and Psychiatry Advisor, symptoms include muscle rigidity, shivering, diarrhea, and even seizures.
One documented case involved a patient taking an SSRI and melatonin who experienced a dramatic spike in blood pressure and severe discomfort—highlighting the need for dose vigilance.
For more on serotonin safety, see: Antidepressants and 5-HTP serotonin syndrome risk
Possible Reduction in Antidepressant Efficacy
Not all interactions are synergistic. A study featured on eMedicineHealth observed that melatonin reduced the therapeutic impact of fluoxetine and desipramine in animals. While human data is limited, this underscores the importance of personalized medical advice.
Common Side Effects from This Combination
Combining melatonin with antidepressants can intensify typical side effects, particularly around sedation and alertness.
Frequently Reported Symptoms:
- Increased drowsiness
- Headaches
- Dizziness
- Stomach discomfort
- Dry mouth or skin
- Irritability
According to WebMD and NHS, these are especially likely when melatonin is taken at higher doses or in the evening with antidepressants that also have sedative effects.
Specific SSRIs and SNRIs to Monitor
SSRIs: Zoloft, Lexapro, Fluoxetine
Zoloft (sertraline) is widely used and often associated with insomnia. While Hims reports no direct interaction with melatonin, it also cautions that the supplement “may make antidepressants less effective.”
The NHS advises patients on SSRIs like fluvoxamine or amitriptyline to speak with a healthcare provider before using melatonin.
SNRIs: Cymbalta, Effexor, Pristiq
SNRIs such as duloxetine (Cymbalta) and venlafaxine (Effexor) are consistently flagged by Drugs.com as having moderate interactions with melatonin. The concern here includes increased sedation and a greater likelihood of experiencing serotonin overload in sensitive individuals.
See also: Mount Sinai‘s melatonin information
Factors That Influence Interaction Severity
1. Dosage of Melatonin
Most adult users are advised to stay below 5 mg per day. Higher doses could increase the risk of drug interactions or exaggerated side effects. According to Mayo Clinic, more isn’t always better.
2. Individual Sensitivity and Medication Regimen
Everyone metabolizes melatonin and antidepressants differently. Those with liver conditions or who are on multiple medications should be especially cautious.
3. Timing of Intake
Taking melatonin too close to antidepressant administration—especially before bedtime—may heighten sedation risks. Staggering the doses under medical supervision might help.
Best Practices for Safe Use
Talk to Your Doctor First
Every major source—including Drugs.com, NHS, and Mount Sinai—recommends consulting a healthcare provider before combining melatonin with SSRIs or SNRIs.
Monitor Symptoms Closely
Be alert to signs of serotonin syndrome, reduced antidepressant effectiveness, or increased fatigue. Consider journaling side effects to discuss during follow-ups.
Use the Lowest Effective Dose
Start with the smallest dose possible and monitor for side effects. Avoid long-term melatonin use without medical guidance, especially in psychiatric care.
Conclusion
The interaction between melatonin and antidepressants such as SSRIs and SNRIs is complex. While melatonin may improve sleep or even enhance mood regulation in some individuals, others may face reduced medication efficacy or increased side effects. The most prudent approach is to use melatonin cautiously and only with the guidance of a healthcare provider.
Explore more on how supplements affect mental health:


