Stockley’s Drug Interactions is a gold-standard reference for healthcare professionals, but its high price and restricted access leave many consumers and smaller clinics searching for an alternative.
Fortunately, several reliable and cheaper drug interaction resources exist, many offering excellent coverage of supplements and herb-drug combinations.
This article highlights trusted consumer drug reference tools that help fill that gap without compromising on quality or evidence.
Summary / Quick Answer
Looking for a Stockley’s interaction reference alternative that doesn’t cost hundreds?
Here are the top-rated free or low-cost options:
- Drugs.com: Free, includes supplement and herb interactions
- Medscape: Registration-only, clinical insights with severity levels
- WebMD: Simple, easy-to-use consumer drug reference
- NIH and PubMed: Deep, evidence-backed resources for supplement interactions
- Natural Medicines: Offers a free chart and sample monographs
These tools are ideal for both clinical reference and personal use.
Why People Look for Stockley’s Alternatives
Stockley’s is a comprehensive drug interaction database used globally by clinicians, pharmacists, and hospitals. It includes:
- Pharmacokinetic and pharmacodynamic data
- Clinical case reports and severity assessments
- Guidance for drug-herb and drug-supplement interactions
However, the subscription cost is steep, often exceeding $600 per year. That’s out of reach for most individuals and even some smaller clinics.
So what can consumers and health-conscious individuals use instead? Let’s break down the best cheaper drug interaction resources that still deliver accuracy, coverage, and ease of use.
1. Online Drug Interaction Checkers for Consumers
Many consumers start with web-based interaction checkers. Here are the most robust options:
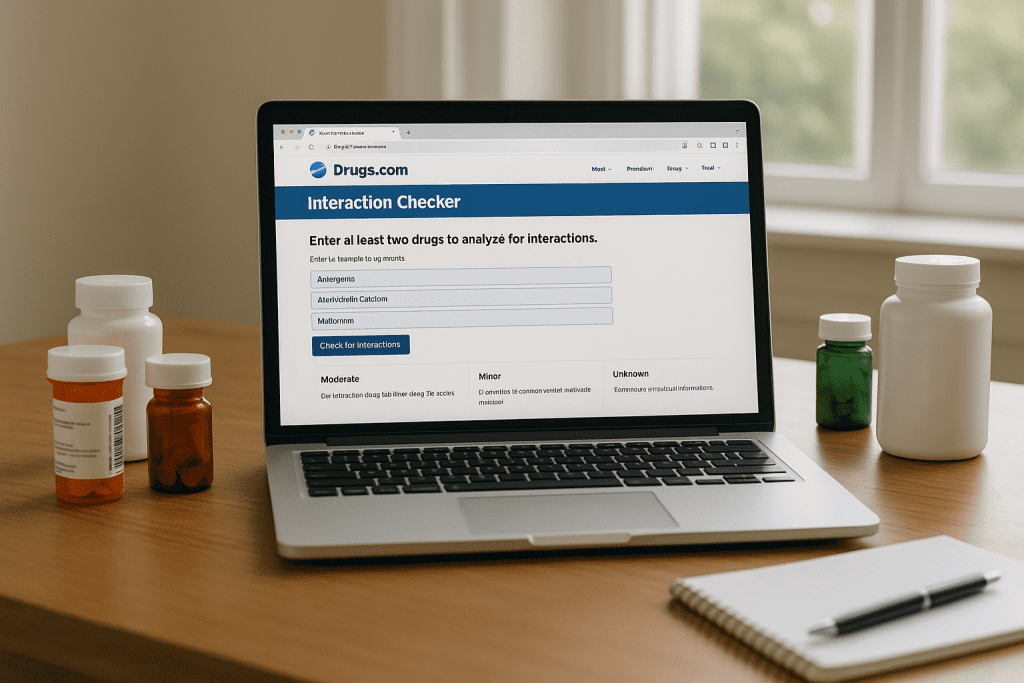
Drugs.com Interaction Checker
Drugs.com offers a free and reliable consumer drug reference that screens interactions across prescription meds, OTC drugs, herbal remedies, and supplements. You can enter multiple items and get:
- Severity ratings (mild to major)
- Management advice
- Descriptions of interaction mechanisms
It covers commonly searched items like St. John’s Wort, turmeric, and green tea extract. Try it here.
Example: A search for “saw palmetto and blood thinner interactions” brings up relevant warnings about additive bleeding risk, linking back to our full article on saw palmetto and blood thinner interactions.
Medscape Drug Interaction Tool
Medscape’s interaction checker is another high-quality option. It requires a quick (free) sign-up but offers clinical-grade details:
- Severity categorization
- Descriptions of interaction type
- Pharmacological insights
It also includes OTC and herbal supplements, giving it a broad scope. Access it here.
WebMD Interaction Checker
WebMD keeps it simple and user-friendly. It allows you to input multiple drugs, vitamins, and supplements and provides:
- Flags for interaction types
- Safety alerts
- Advice for consumers
Visit the WebMD tool for quick answers.
Comparison Table
| Tool | Supplements Included? | Clinical Detail | Free to Use? |
|---|---|---|---|
| Drugs.com | Yes | Moderate | Yes |
| Medscape | Yes | High | Yes (sign-up) |
| WebMD | Yes | Basic | Yes |
2. Evidence-Based Supplement Interaction Databases
For more detailed analysis of supplement-related interactions, consider databases backed by peer-reviewed research.
Natural Medicines (Therapeutic Research Center)
While mostly paid, Natural Medicines offers a free interaction chart summarizing over 100 common supplement-drug interactions with:
- Interaction types (e.g., additive, antagonistic)
- Severity ratings
- Clinical examples
Find the chart here.
Some sample monographs (like those on St. John’s Wort or garlic) are also accessible without a subscription.
University and Clinical Open Sources
Several universities maintain monographs and open-access guides for health students and clinicians:
- University of Minnesota Herb-Drug Interaction Monographs
- Merck Manual Dietary Supplement Interaction Table
These can help you verify possible issues like “muscle cramps from diuretics and potassium supplements”, as explored in our full article here.
3. Academic and Government-Verified References
Beyond commercial checkers, government and academic sources provide open access to in-depth interaction data.
PubMed and NIH
The NIH Office of Dietary Supplements publishes consumer fact sheets for nutrients and herbs, including known risks. For example:
- Calcium–thiazide diuretic interaction
- Garlic–blood thinner interaction
PubMed and PMC also offer full-text reviews, like those evaluating vitamin D’s interaction with drugs.
Supp.AI
This AI-powered search tool tracks emerging interactions by indexing new biomedical literature. While not a replacement for clinical advice, it’s ideal for researchers or advanced users wanting the latest data. Learn more here.
Key Considerations Table
| Resource Type | Evidence-Based? | Supplement Focus | Free Access? |
| PubMed / PMC | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| NIH ODS Fact Sheets | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Supp.AI | Yes | Yes | Yes |
How to Choose the Right Interaction Tool
If you’re not a clinician, the right tool for you depends on your goal:
- Quick safety checks? Try Drugs.com or WebMD.
- More clinical depth? Use Medscape or Natural Medicines.
- Scientific details? Explore NIH fact sheets or PubMed articles.
Also, double-check results across platforms. Just because a tool flags an interaction doesn’t mean it’s clinically relevant – context matters. For example, some interactions might depend on dosage or duration.
And remember, certain nutrients can intensify drug effects even if they seem “natural.” That’s why it’s vital to research interactions like potassium supplements with ACE inhibitors or diuretics.
Conclusion
You don’t have to pay a premium to access trustworthy drug and supplement interaction data. From free online checkers like Drugs.com and Medscape to academic resources from NIH and PubMed, there are numerous Stockley’s interaction reference alternatives that offer clear, evidence-based insights.
For health-conscious consumers, combining quick online tools with deeper research from government databases ensures both breadth and credibility.
Looking to understand better how supplements interact with medications? Check out these posts:

