Magnesium is essential for sleep, mood, muscle function, and heart health – yet magnesium deficiency is more common than many realize. This guide explores the types of magnesium, what they’re best used for, and how to find the right dose for your needs.
If you’re curious whether you’re getting enough or which supplement offers the best results, the science here can help you decide.
Summary / Quick Answer
Here’s a quick breakdown of magnesium benefits, deficiency signs, and top supplement forms:
Common Magnesium Deficiency Symptoms:
- Fatigue, anxiety, poor sleep, muscle cramps, irregular heartbeat
Top Magnesium Supplement Types:
- Glycinate – great for sleep, anxiety, and gentle digestion
- Threonate – best for brain and memory support
- Citrate – excellent for digestion and general use
- Taurate – heart health and blood pressure
- Malate – energy and muscle pain
Dosage Recommendations:
- Adults typically need 310–420 mg daily
- Safe upper intake: 500 mg/day (supplements)
- Take in divided doses to improve absorption
Learn how to identify magnesium deficiency
Understanding Magnesium Deficiency
Many adults aren’t getting enough magnesium, and the consequences show up in ways you might not expect.
Magnesium is involved in over 300 enzyme systems. It supports sleep regulation, energy production, and nerve signaling. But modern diets (high in processed foods, low in greens, nuts, and legumes) often fall short. According to the NIH, 48% of Americans consume less than the recommended amount.
Common Signs of Magnesium Deficiency
- Sleep issues: trouble falling or staying asleep
- Muscle symptoms: cramps, twitches, or weakness
- Mood issues: anxiety, irritability, low stress tolerance
- Fatigue: general lack of energy, sluggishness
- Heart symptoms: palpitations, high blood pressure
Learn how to identify magnesium deficiency
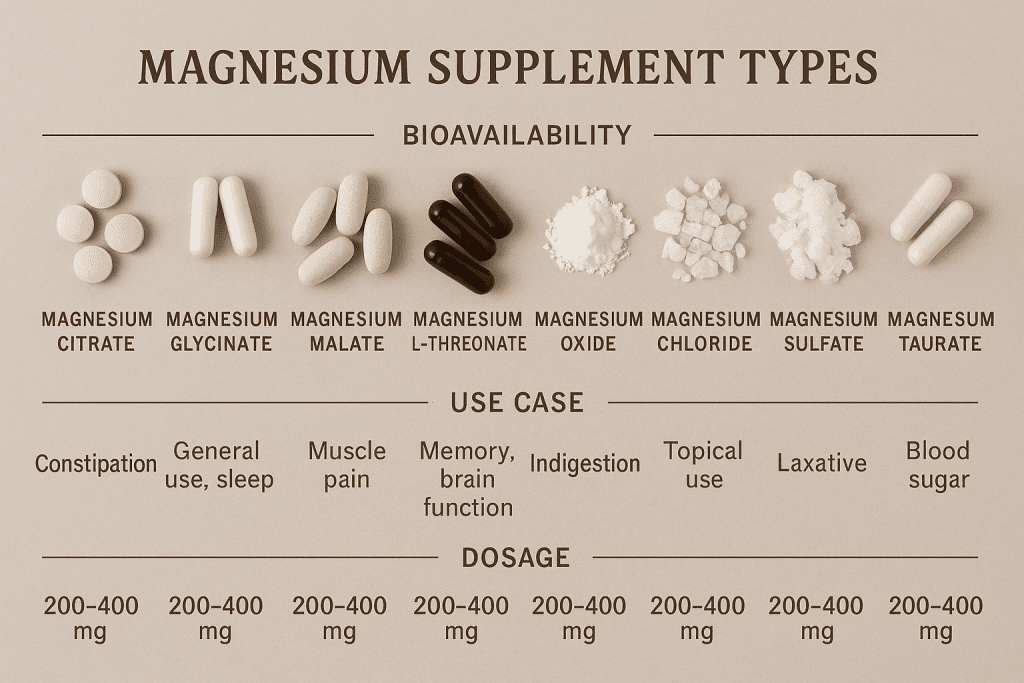
Comparing the Types of Magnesium Supplements
Not all magnesium is created equal. While some forms absorb well and suit sensitive digestion, others offer specific therapeutic benefits (like crossing the blood-brain barrier).
| Magnesium Type | Bioavailability | Best For |
|---|---|---|
| Glycinate | ~80% | Sleep, anxiety, gentle on stomach |
| Threonate | ~85% | Brain function, memory, sleep |
| Citrate | ~90% | Constipation, general use |
| Taurate | ~65% | Heart health, blood sugar |
| Malate | ~70% | Energy, muscle soreness |
| Chloride | ~75% | General use, topical use |
| Orotate | ~60% | Athletic performance, heart |
| Oxide | ~25% | Occasional constipation |
Note: Oxide has the highest elemental magnesium but the lowest absorption. Don’t confuse content with effectiveness.
Health Benefits of Magnesium by Form
Each magnesium form brings unique benefits based on how it’s processed and absorbed by the body. The research says this.

Magnesium Glycinate: Sleep and Stress Relief
Magnesium glycinate is highly absorbable and combines magnesium with glycine – a calming amino acid. It’s widely used for:
- Supporting deep, uninterrupted sleep
- Easing anxiety and chronic stress
- Reducing muscle tension
- Gentle digestion – great for sensitive stomachs
Glycinate is a top choice if your main concern is sleep or anxiety, and it’s better tolerated than citrate or oxide.
Explore magnesium’s role in anxiety
Magnesium Threonate: Cognitive and Brain Health
Threonate is the only form that crosses the blood-brain barrier effectively. Developed at MIT, it helps:
- Improve memory and learning
- Enhance sleep quality (especially REM)
- Support brain aging and neuroplasticity
If your focus is brain fog, aging-related memory, or even ADHD, threonate may be the best fit.
Magnesium Citrate: Digestive Health and General Use
Citrate offers a balance between absorption and affordability. It helps:
- Relieve constipation gently
- Support bone and heart health
- Replenish magnesium levels efficiently
It’s a go-to for general supplementation and is widely available.
Magnesium Malate: Energy and Muscle Support
By combining magnesium with malic acid (involved in ATP production), malate can:
- Boost energy
- Reduce muscle pain and soreness
- Aid fibromyalgia symptom management
It’s particularly useful for those with chronic fatigue or active individuals recovering from workouts.
Magnesium Taurate: Cardiovascular Function
Taurate combines magnesium with taurine, an amino acid that also supports heart health. It may:
- Regulate blood pressure
- Support heart rhythm
- Aid blood sugar control
This form is often recommended for people with metabolic syndrome or cardiovascular concerns.
Learn how magnesium supports the heart
Dosage Recommendations and Timing Strategies

How Much Magnesium Do You Need?
| Group | Recommended Daily Amount |
| Adult Men (31+) | 420 mg |
| Adult Women (31+) | 320 mg |
| Pregnant Women | 350-360 mg |
| Teens (14–18) | 360–410 mg |
Most people benefit from 300–400 mg/day from food and supplements combined. A recent review found up to 500 mg/day from supplements is well tolerated for healthy adults (source).
Best Timing
- Split your dosage into 2 servings (morning + evening)
- Take with food to reduce stomach upset
- For sleep: take 1–2 hours before bed
Side Effects, Interactions, and Safety
Magnesium is generally safe – but too much or the wrong form can cause side effects.
Common Side Effects
- Diarrhea or loose stools (common with oxide, citrate)
- Nausea or bloating
- Cramps if dosing too high too fast
Start low and increase gradually. Glycinate is best tolerated.
Medication Interactions
Magnesium can interfere with several medications:
- Antibiotics – may reduce absorption
- Diuretics – may increase or decrease magnesium levels
- Bisphosphonates – used for osteoporosis
Always space supplements and medications by 2+ hours, and check important medication interactions.
Who Should Be Cautious?
- People with kidney disease
- Pregnant or breastfeeding women (consult doctor)
- Elderly – due to possible medication overlap
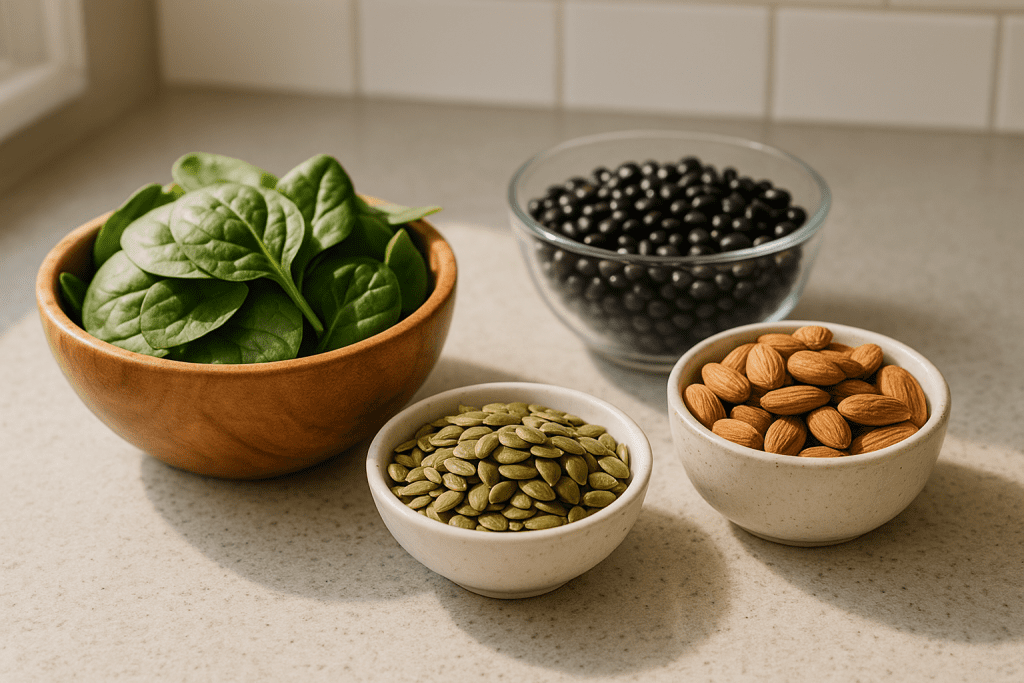
Food Sources of Magnesium
Before reaching for a supplement, consider what’s on your plate. These foods are rich in magnesium:
| Food | Magnesium per serving |
| Pumpkin seeds (1 oz) | 168 mg |
| Chia seeds (2 tbsp) | 95 mg |
| Almonds (1 oz) | 80 mg |
| Spinach (1/2 cup) | 78 mg |
| Black beans (1/2 cup) | 60 mg |
Magnesium from food is absorbed well, especially when combined with vitamin D and calcium-rich foods.
Conclusion
Magnesium is one of the most versatile nutrients in the human body. Its benefits are hard to ignore, ranging from better sleep and stress control to muscle performance and heart rhythm support.
The right form matters. Choose magnesium glycinate or threonate for calm and cognition, taurate for heart health, or citrate for digestion and general use. Dosing should match your needs and be spaced throughout the day for optimal absorption.
To explore specific concerns, check out Magnesium and Heart Health or Best Magnesium for Sleep.

