Navigating supplements while breastfeeding can be confusing, especially if you’re also taking postpartum medications. Are your vitamins helping or possibly interacting with your meds? This article answers those questions clearly.
We break down lactation-safe supplements, explore how vitamins interact with common postpartum drugs, and provide science-backed guidance for nursing mothers.
If you’re wondering whether your daily multivitamin or omega-3 capsule is safe—or if something like St. John’s Wort could be risky—you’re in the right place.
Summary / Quick Answer
What are lactation-safe supplements when you’re on postpartum meds? Here’s a quick guide:
- Safe and beneficial:
- Vitamin D (10 mcg/day)
- Folic acid (400 mcg/day if not on contraception)
- Standard multivitamin (within RDA limits)
- Omega-3 fatty acids
- B vitamins (including B12)
- Vitamin C (especially if on opioids)
- Use caution or avoid:
- Vitamin A above 700–800 mcg/day
- St. John’s Wort, garcinia cambogia, kava, valerian (if on SSRIs)
- Vitamin E (if taking NSAIDs like ibuprofen or aspirin)
- Excess iodine (>100% RDA)
Always consult a pediatrician or OB before introducing supplements while nursing and medicated.
Breastfeeding Nutritional Demands and Supplement Basics
Breastfeeding significantly increases your body’s nutritional demands. You’re not only supporting your own recovery but also fueling your baby’s growth through your milk. The right supplements can help, but not every pill is safe to take while on medications.
What Should You Take?
The foundation of lactation safe supplementation includes:
- Vitamin D: Required daily, even with a healthy diet. The NHS and CDC recommend 10 mcg/day during lactation.
- Folic Acid: Especially important if you’re not using contraception postpartum.
- Multivitamins: Not essential for everyone, but practical whenthe diet is inconsistent.
If you’re vegetarian or vegan, vitamin B12 becomes essential due to its absence in plant-based foods. According to the CDC, supplementation ensures adequate levels in your milk.
Calcium needs stay steady at 1,000–1,300 mg/day. Surprisingly, your body adjusts absorption during lactation, so extra calcium isn’t always necessary.
Think of a multivitamin as your nutritional backup—not your first line of defense. Whenever possible, prioritize whole foods.
Related: Fatigue from iron supplements and thyroid meds
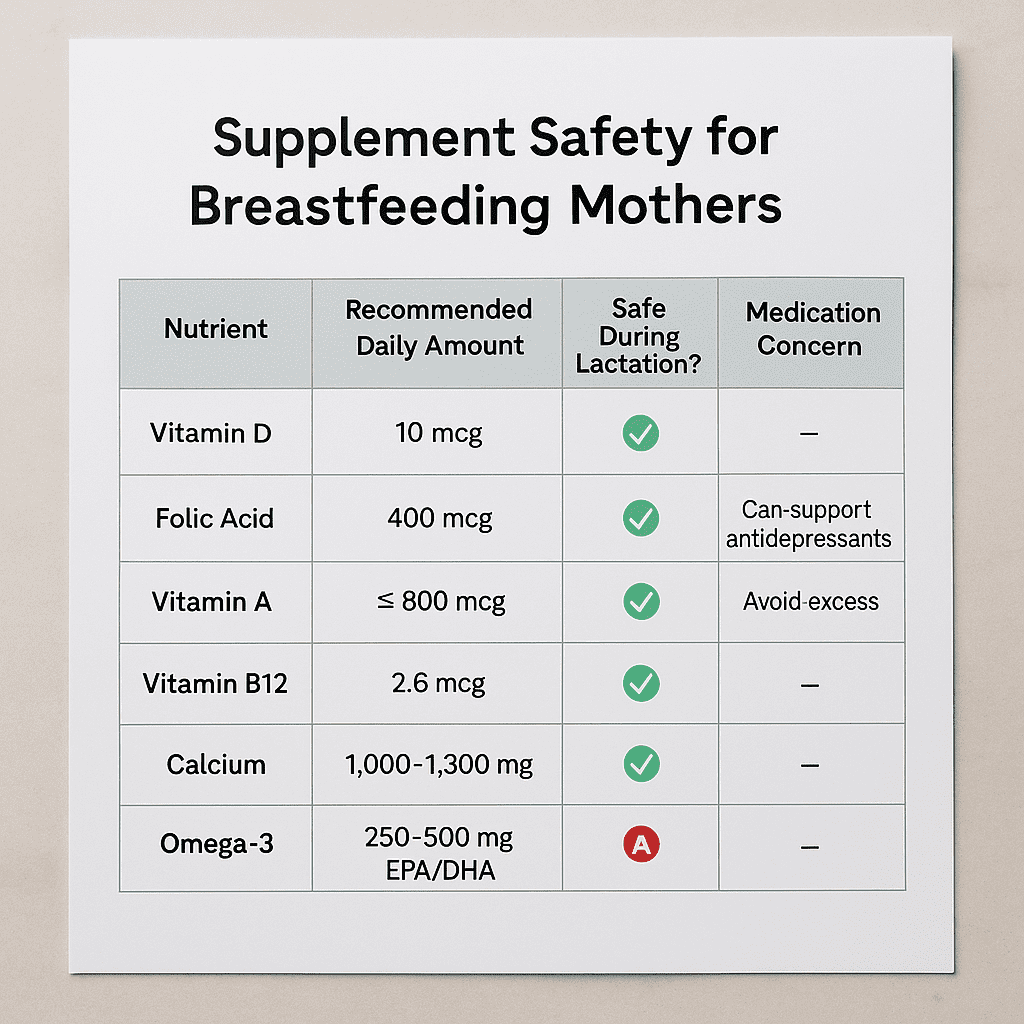
Table: Core Supplements Recommended While Breastfeeding
| Nutrient | Recommended Daily Amount | Safe During Lactation? | Medication Concern? |
|---|---|---|---|
| Vitamin D | 10 mcg | ✅ Yes | None |
| Folic Acid | 400 mcg | ✅ Yes | Can support antidepressants |
| Vitamin A | ≤ 800 mcg | ✅ Yes (in moderation) | Avoid excess |
| Vitamin B12 | 2.6 mcg | ✅ Yes | Essential for vegans |
| Calcium | 1,000–1,300 mg | ✅ Yes | No increase needed |
| Omega-3 | 250–500 mg EPA/DHA | ✅ Yes | Can benefit SSRIs |
Drug-Supplement Interactions Nursing Mothers Should Know
If you’re on postpartum meds, especially SSRIs or pain relievers, some supplements can either help or harm.
Vitamins That Support Antidepressants
Selective Serotonin Reuptake Inhibitors (SSRIs) are the most common postpartum antidepressants. Certain nutrients may boost their effectiveness, including:
- Omega-3 fatty acids: A meta-review from the University of Melbourne found that omega-3s improve antidepressant outcomes.
- Vitamin D and methylfolate: Both support neurotransmitter health and can improve SSRI efficacy.
- SAMe: A bioactive compound that may complement SSRI therapy.
This is where postpartum medication vitamin synergy comes in: some supplements work with, not against, your prescriptions.
Supplements to Avoid with SSRIs
Be cautious with:
- St. John’s Wort & garcinia cambogia: Can dangerously raise serotonin levels, risking serotonin syndrome.
- Kava & valerian: Increase sedation and impair daily function when mixed with SSRIs or benzodiazepines.
These risks are well-documented in sources like the NHS and ConsumerLab.
Also See: Vegan supplements and thyroid medication absorption
Pain Relievers and Supplement Timing
Postpartum recovery often comes with pain. Whether you’re prescribed NSAIDs or opioids, it’s smart to ask how supplements might affect your meds.
NSAIDs (e.g., ibuprofen)
- Vitamin E has blood-thinning effects, just like NSAIDs.
- Taking both could increase bleeding risk, especially in higher doses.
- Studies like this one from PMC highlight this interaction clearly.
If you’re taking aspirin or ibuprofen, talk to your doctor before adding vitamin E.
Opioids
- Vitamin C may help counteract some side effects of opioids, including oxidative stress and immune suppression.
- Early evidence from PubMed supports its use—but always confirm with your OB or pediatrician.
Smart Supplementation Rules for Nursing Moms on Meds

Let’s simplify the safest path forward:
Do:
- Choose standard multivitamins within the recommended daily values
- Include B vitamins, particularly B12, for energy and mood
- Add omega-3s if on antidepressants
- Take vitamin C with opioids (if approved by your doctor)
Avoid:
- Mega-doses of any vitamin, especially:
- Vitamin A > 800 mcg/day
- B6 > 20–50 mg/day
- Iodine above 100% RDA
- Herbal supplements unless cleared by a doctor
Always bring your full supplement list—including protein powders or energy drinks—to medical checkups.
Conclusion
Supplementation can be both safe and helpful for nursing mothers on postpartum medications—when done thoughtfully. Vitamin D, folic acid, multivitamins, B12, and omega-3s are typically well tolerated and may even support treatment. But be cautious: certain herbal supplements and high-dose vitamins may carry real risks.
Always aim to meet nutritional needs through diet first. When that’s not enough, supplement smartly—with guidance from your healthcare team.
Next Reads on UsefulVitamins.com

